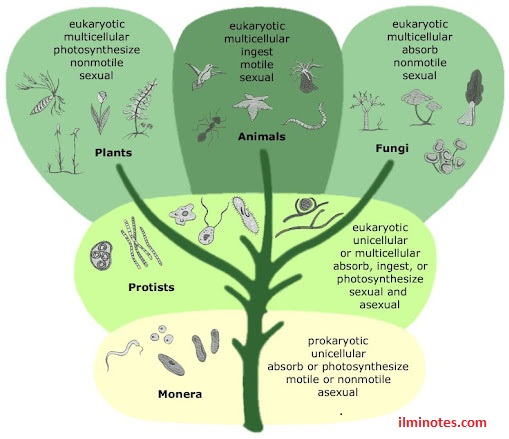
Today, scientists divide living things into five major groups called Five Kingdom Classification System. These kingdoms were named as Monera, Protista, Fungi, Animalia and Plantae.
Five Kingdom Classification System Examples
|
Kingdom |
Example |
|
Monera |
Bacteria |
|
Protista |
Algae |
|
Fungi |
Yeast, mushrooms,
etc. |
|
Animalia |
Animals |
|
Plantae |
Plants |
Kingdoms of Living
Things
Living things are
classified into two Kingdoms:
- The plant kingdom
system includes bacteria, fungi, algae, and plants.
- The animal kingdom includes single-cell priorities and cell-free animals.
The five kingdoms System represent a group of objects living
which has common characteristics. The characteristics of the five-kingdomclassification system are as follows:
Kingdom Monera
It includes prokaryotic
organisms i.e. they are made of prokaryotic cells. Monera are unicellular. Some
types of Monera forms chain or colonies of cells. Prokaryotic cells are different from eukaryotic cells. Most are
heterotrophic but some Perform Photosynthesis because they have chlorophyll in their cytoplasm.
There are two types of Monera Bacteria and Cyanobacteria.
Kingdom Protista
Kingdom Protista includes eukaryotic unicellular and simple multicellular organisms. There are three main types of Protista
· Algae are unicellular, colonial or simply multicellular. They are similar to plant cells with cell walls and chlorophyll in chloroplasts. Simply multicellular means that they do not have multicellular organs and do not form embryos during their life cycle.
· Protozoa are similar to animals whose cells lack of chlorophyll and cell walls.
· Some protists are fungus-like.
Kingdom
Fungi
Kingdom Fungi includes eukaryotic multicellular heterotroph
that is absorbed in a nutrient mode, for example. Mushroom. Most fungi are
decomposers. They live on organic matter, secrete digestive enzymes, and absorb
small organic molecules produced by enzyme digestion.
Kingdom Plantae
Kingdom Plantae
includes eukaryotic multicellular autotrophs. Plants are nutritionally
self-supporting and make their own food through photosynthesis. They have
multicellular organs and form embryos during their life cycle. This kingdom
includes mosses, ferns and flowering plants.
Kingdom Animalia
(animals)
The animal kingdom includes eukaryotic multicellular
consumers. Animals live mainly by eating food and digesting it in a special
cavity. They have no cell walls and they have movement.
Characteristics of the Five Kingdom
Classification System by Robert Whittaker
This system was proposed by Robert Whittaker in 1969. It is a
old system of classification. This classification system is based on two
principles:
1.
Three levels of organizations: cellular,
tissue, and organ level.
2.
Three principle mode of nutrition: photosynthesis, absorption, and ingestion.
Kingdom Monera
It
contains all the prokaryotic unicellular organisms. It includes bacteria and blue-green algae.
Kingdom Protista
They
are eukaryotes. All the organisms which do not come in the definition of
plants, animals, or fungi are in this kingdom. Most of
the protists are unicellular like Euglena and Amoeba. This kingdom system also contains simple multicellular organisms.
Kingdom Plantae
This kingdom includes all eukaryotic
multicellular autotrophs. Plants are self-supporting. They synthesize their own
food through photosynthesis. This includes mosses, ferns, and flowering plants.
These are eukaryotic
multicellular reducing agents. Fungi are heterotrophic organisms. They have a
mode of nutrient absorption. Most fungi are decomposers. They live on organic
materials. They secrete (t/L) digestive enzymes. These enzymes break down
organic matter into smaller organic molecules. Fungi absorb these organic
molecules.


Post a Comment