Plants are an important part of the ecosystem. Every living thing which is present on the earth directly or indirectly depends on plants. The most important part of the plant is leaves.Types Of Leaves
Types of Leaves
 |
| Types Of Leaves |
Simple Leaf
When a single leaf is connected to the main stem by a petiole, the leaf is considered simple. A simple leaf can be cut to any depth, but not to the midrib or petiole. Such as guava leaves
Compound Leaf
Compound leaves are leaves composed of two or more leaflets. In compound leaves, the central vein of the leaf is divided into individual leaves and attached to a single stem. For example, peas, palm leaves.
Structure of a Leaf
Leaves are thin and flat organs responsible for photosynthesis. It was later developed on the node. It is an important part of the bud system, and the bud originates from the apical meristem.
The following describes the structure of the leaf in detail:
 |
| Types Of Leaves |
Parts of a Leaf
Leaf base: This part of leaf attached to the stem. It is composed of two small leaf-like structures called stipules. In rice, wheat, and other monocots, it is wide and covers the stem.
Petiole: The petiole is a long, thin, that connects the leaf and stem.
Blade:It is also called blade. It has a green flat surface. It consists of a small branch vein and veins. The vein running in the middle of the lamina is called the median vein. The midrib divides the lamina into two parts. These veins give the leaves rigidity and facilitate the transportation of water and other substances.
Modification Of Leaves
We know that the leaves are used exclusively for photosynthesis. They also play other important roles, such as support, food storage, defense, etc. For each of these functions, they have been modified in various forms.For example, the tendrils of peas, the thorns of cacti, the bulbs of onions, and the leaves of insectivorous plants are all modified leaves. Modifications of the leaves in detail are given below:
 |
| Types Of Leaves |
Storage leaves
Xerophytes and sedum plants have thick, succulent leaves that can store water in their tissues. The parenchymatous cells of these leave contain large vacuoles filled with hydrocolloids. This modification helps the plant resist drying out.
Leaf tendril
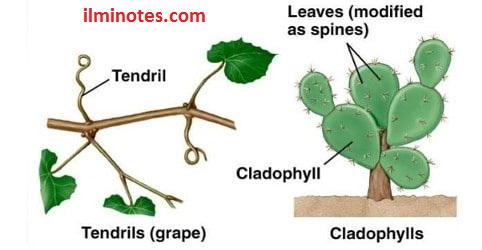
Leaf tendrils are found in plants with weak stems. The leaves become linear structures called tendrils. These tendrils are installed on nearby sticks or walls and support plants. For example, in Lathyrus aphaca, the entire leaf becomes tendrils. The upper leaves of the pea become tendrils.
Leaf thorn
The leaves of some plants are modified into needle-like structures called spines. The thorn serves as a protective structure. They can also reduce water loss due to transpiration. For example, in a cactus, the leaves become spines.
Scale leaves
These are thin membranous structures with no stems and are brown or colorless in appearance. They protect the support buds on the axe. The scales and leaves of onions are thick and can store food and water. Casuarina and asparagus also sell leaves.
Leaflet Hooks
In some plants, the terminal leaflets of the leaves become hook-like structures to help them climb. For example, Bignonia unguiscati.
Leaf root
In some plants, one of the leaves on the node will transform into adventitious roots, helping them to float on the water. For example, Salvia
Function of leaves
The leaves perform the following functions:
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the main function of leaves. They convert carbon dioxide, water, and ultraviolet light into glucose through photosynthesis.
See also: photosynthesis
Transpiration
It is the transfer of excess water from plants to the atmosphere. This happens by opening the stomata present in the leaves.
Guttation
When the stomata are closed, the removal of excess water from the xylem at the edge of the leaf is called guttation.
Store
Leaves are the place of photosynthesis. Therefore, they store water and nutrients. The juicy and thick leaves are suitable for water storage.
Defense
Some leaves are changed into spines to protect them from damaged or eaten by animals. For example, cactus.

Post a Comment